Editorial Note: This article is written with editorial review and topic relevance in mind.
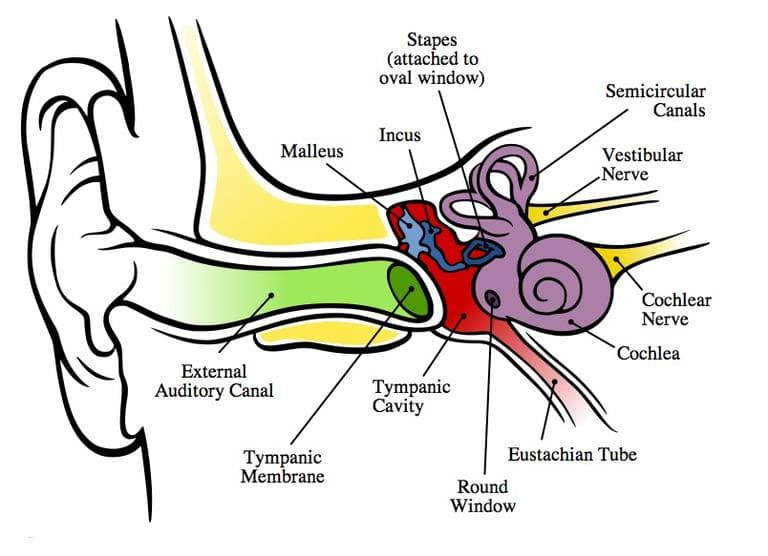
At the deep end of the external acoustic meatus, separating the external ear from the tympanic cavity (of the middle ear) lies the tympanic membrane (eardrum). The external, middle and internal ear. The middle ear is a complex system of.
Eardrumspasm xeenagilmo
The outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. Learn the anatomy of the ear, including the external, middle and inner ear and the auditory tube. The outer ear consists of the auricle, the visible outer part, and the ear canal.
This sensory organ is made up of the outer, middle, and inner ear.
The ear is the sensory organ for hearing and balance and it is anatomically divided into 3 parts: Anatomically, the ear has three distinguishable. Explore structure, function and clinical relevance for medical learning. In the normal ear, the tympanic membrane vibrates from sound, the three bones.
It’s shaped a bit like a cone, protruding slightly into. The middle ear space contains the three bones of hearing, the malleus (“hammer”), incus (“anvil”) and stapes (“stirrup”). The tympanic membrane is also called the eardrum, and it’s a thin, translucent membrane that separates the external ear from the middle ear. Human ear, organ of hearing and equilibrium that detects and analyzes sound by transduction and maintains the sense of balance.

In humans, the ear is described as having three parts:
Learn about what each part does, how hearing and balance work, and common ear conditions. Learn how the ear works, explore its anatomy, functions, and disorders, and download free ear diagrams, worksheets, and a glossary.